Global Uncertainty and Sensitivity Analyses of Habitat and Metapopulation Models
Ma Librada Chu-Agor (University of Florida, ABE Dept. - IFAS)
SLAMM (Sea Level Affecting Marshes Model) is widely used to simulate wetland conversion and shoreline modification for the purpose of habitat vulnerability assessment and decision making. RAMAS model on other hand simulates the future of the metapopulation for extinction risk assessment, viability analysis and wildlife management. Prior to linking these two models together, a systematic exploration of the input-output relationship through global sensitivity and uncertainty analyses is necessary in order to identify and understand the dominant processes driving the system being modeled by each one. This is essential before any conservation and restoration efforts can take place. In addition, understanding the input-output relationship of these models will ensure a more efficient use of resources (in terms of research prioritization and data collection) as well as the reliability of the entire modeling process.
This study presents a generic evaluation framework consisting of a state-of-the-art screening and variance-based global sensitivity and uncertainty analyses of SLAMM and RAMAS in order to:
- Identify the important input factors and processes that control the model's output uncertainty.
- Quantify the model's global output uncertainty and apportion it to the direct contributions and interactions of the important input factors.
- Evaluate this new methodology to explore the potential fate of the coastal habitats of the study area and the population of Snowy and Piping Plovers
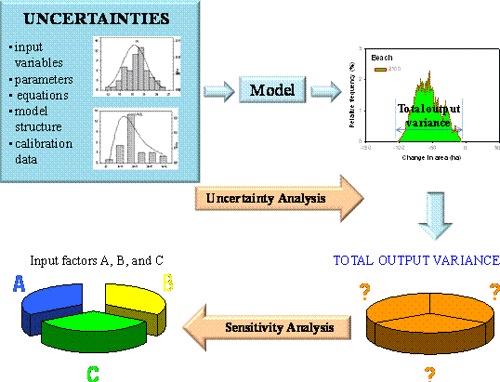
Figure 5. Global uncertainty analysis propagates all the uncertainties, using a model, to the
model's outputs while sensitivity analysis determines the contribution of each input factor
to the uncertainty of the outputs.
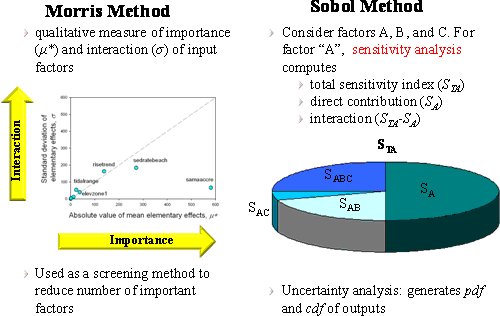
Figure 6. Global sensitivity and uncertainty analysis (GSA) is carried out using a state-of-the-art
screening method (Morris method) and a variance-based global sensitivity and uncertain technique
(Sobol method). Morris screening method provides a qualitative ranking of the model's input factors
that drive output variability while the Sobol method quantifies the contributions and interactions
of the input factors to the variability of the output.
Figure 7. Piping (migratory) and Snowy Plovers (resident) in Florida.
This page was last updated on July 13, 2019.